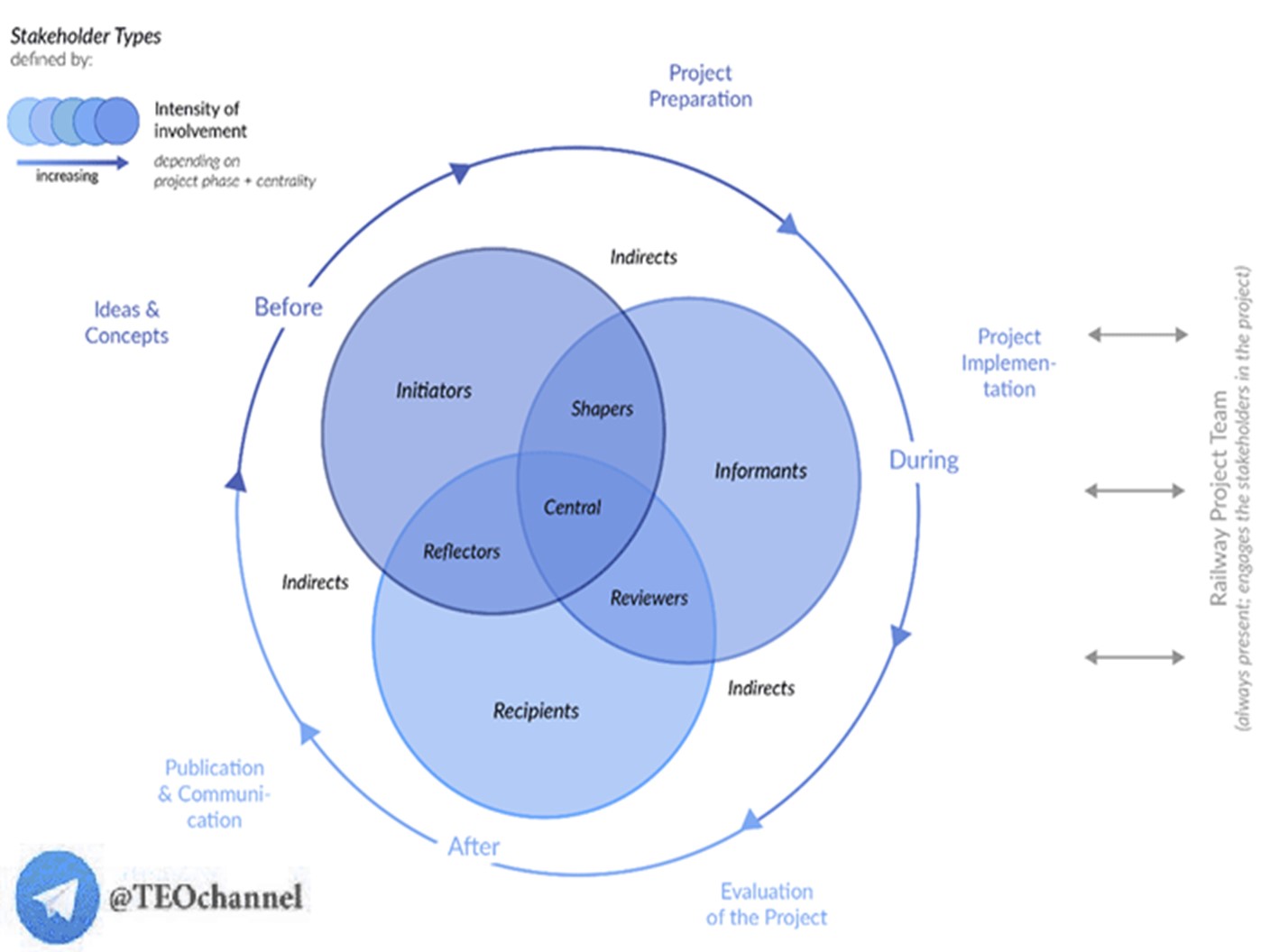
Using integrated solutions as
market-shaping/market-driving strategy in oil industry
Part 4
استفاده از "راه حل یکپارچه" به عنوان استراتژی شکل دهنده بازار و
هدایت کننده بازار در صنعت نفت
بخش چهارم
لینک بخش 3
این پژوهش به عنوان تز پایانی دوره MBA در یکی از دانشگاه های مطرح اروپایی ارایه شده است
Strategy in
Uncertain Environments
The essence of any decision is
uncertainty (Drucker, 2002). In strategic
planning or any other type of planning, a manger should deal with the concept
of “Future” and accompanying with future there is always concept of
uncertainty. The high level of uncertainty aftermath of recent downturn and its
consequences have made traditional strategy tools unrelated or at least less
useful. Here, some of the tools, methods, strategy postures and moves proposed
by literature in face of uncertainty, are presented.
Historically, the US Army
established and advanced scenario planning and war gaming in 1950s. Later,
quantitative techniques, decision trees and probability-based net-present-value
calculations have been studied since 1960s. Although these tools are valuable,
the challenge of managing uncertainty needs more than just thorough analysis
produced by them (Bryan, 2009).
Flexibility and its importance are one of the most popular factors that
researchers have mentioned in context of uncertainty. Flexibility moves
increase internal responsiveness without changing the predictability of
external factors and they are identified as flexibility in operation and
diversification (Miller, 1992) (Wernerfelt & Karnani, 1987) (Enderwick, 2006) (Lowell & Farrell, 2008).
The other strategy suggested in face
of uncertainty is created based on the notion that to the degree that the
future is shaped there is no need to predict it (Sarasvathy,
2001 ).
Firms may pursue to control environmental contingencies to reduce uncertainties
(Cyret and March 1963, Mascarenhas 1982, as cited in Miller, 1992). MacCrimmon
and Wehrung (1986) research present that managers are inclined to control
uncertainty instead of accepting it as a given limitation. Examples are
political activities, achieving market power and forcing competitors into more
predicable patterns of behavior (as cited in Miller, 1992). The use of market
power to prevent entry of new entrants is the main method suggested by Porter
(1980, 1985) to manage uncertainty (Miller, 1992). Making alliance
with complementary products’ suppliers, co-opt with rivals, making bold mergers
and acquisitions, making alliances and joint ventures, multilateral
agreements are some of the strategic
moves to bring certainty to the market (Miller, 1992) (Hamel & Prahalad, 1995) (Courtney et
al, 1997) (Courtney,
2001).
Hamel (1996,1997) proposes “strategy as revolution” in which companies should not play by the
rules of the industry, instead they should transform “ the basis of competition
in their industry” and brings the examples of IKEA, Dell and Southwest Airlines
as rule breakers that are “overturning
the industrial order” (as cited in Mintzberg et al, 1998). In addition, he
criticizes industry analysis and focusing on direct competitors as path to
strategy formation, since due to complexity of new business world identifying
business and industry boundaries, and distinguishing competitors from
collaborators became very hard (Hamel & Prahalad, 1994). Kim and Mauborgne
(2005) introduce blue ocean strategy which suggests a systematic approach to
make competition irrelevant. Red ocean strategists concentrate on making
competitive advantages usually through analysis of competitors’ way of doing
things and struggling to perform it better. Blue ocean strategists believe that
boundaries exist in people’s minds so they do not allow existing market
structures restrict them. They believe that abundant demand is out there,
untouched waiting for them and their job is to create them. In addition, since
market structures can be transformed via destroying the value-cost system, consequently
the rules of games would be broken as well and competition via old rules
becomes irrelevant (Insead , 2005) (Kim & Mauborgne, 2005).
Paradoxically, there are some ideas
about favoring and encouraging uncertainty by some groups of business leaders
which are in line with controlling and shaping uncertainty. Some entrepreneurs
believe that being in an uncertain environment implies that the market could be
shaped via their decisions
and moves working in cooperation with pre-committed stakeholders and
customer-partners (Sarasvathy, 2001 ).
DiMaggio and Powell (1983) state
that imitation of pioneers in industry (or follow-the-leader) as other
strategic choice for companies facing uncertainty (as cited in Miller 1992).
Courtney et al (1997) and Courtney (2001) define adaptation as a strategic
posture against uncertainty and one of the adaptors’ methods is to follow a
leader (shaper). The other strategy under uncertain condition is avoidance
which includes divestment for already active firms and postponement of market
entry for not active yet companies (Miller, 1992) (Courtney et al, 1997) (Enderwick,
2006).
Highly uncertain conditions –like aftermath of the recession- may cause to form
too risk-averse strategies so business leaders should be careful that this
would not cause firm to miss out valuable opportunities (Gjetsund et al, 2010).
One of the issues which have been
mentioned in forming strategy under uncertainty is insufficiency of standard
tools in this area. For example Porter five forces, discounted cash flow and
core competency diagnostics could provide “ insight” into strategic opportunities
in stable markets they do not offer deep
“foresight” into opportunities in uncertain and changing environments. Then,
without this foresight, managers cannot outline the future they want to make (Courtney,
2001).
Anthony et al (2008) express that in environments with low certainty using
financial models and making all discussions on financial projections is waste
of time. Furthermore, in establishing analytical priorities, some critical
uncertainties cannot be clarified via more research (Bhide,
1994).
لینک به بخش 5..
منابعی که با رنگ آبی مشخص شده اند قابل دریافت می باشند.
References:
Bhide, A. (1994). How Entrepreneurs Craft Strategies
That Work? HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW March-April 1994, 150-161.
Bryan, L. (2009). Dynamic management Better decisions
in uncertain times. McKinsey Quarterly, the business journal of McKinsey
& Company, 50-62.
Courtney et al. (1997). Strategy Under Uncertanity . Harvard
Business Review, 66-79.
Courtney, H. (2001, November). Making the most of
the uncertainty. Retrieved 2011, from McKinzey Quarterly:
http://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/Making_the_most_of_uncertainty_1128
Drucker. (2002). Innovation and Entrepreneurship
Practice and Principles. New York: HarperCollins.
Enderwick, P. (2006). Managing the new global threats.
University of Auckland business review, 62-72.
Gjetsund et al. (2010). Strategic Planning in an
Age of Uncertainty. Retrieved 2011, from Accenture:
http://www.accenture.com/us-en/Pages/insight-strategic-planning.aspx
Hamel, G., & Prahalad, C. (1994). Competing for
the Future. Boston: HBS Press.
Hamel, G., & Prahalad, C. K. (1995). Thinking
differently. Business Quarterly, 22-35.
Insead . (2005). Alumni/Newsletter/. Retrieved
2011, from Insead The Business School:
http://www.insead.edu/alumni/newsletter/February2005/Interview.pdf
Kim, C., & Mauborgne, R. (2005). Blue Ocean
Strategy How to Create Uncontested Market Space and Make the Competition
Irrelevant . Boston: Harvard Business School Publishing Corporation.
Lowell, B., & Farrell, D. (2008). Leading
through uncertainty. Retrieved 2011, from McKinsey Quarterly-McKinsey &
Company: http://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/Leading_through_uncertainty_2263
Miller, K. (1992). A Framework for Integrated Risk
Management in International Business. Journal of International Business
Studies, 311-332.
Mintzberg et al. (1998). Strategy Safari: A Guided
Tour Trough the Wilds of Strategic Management", Bruce Ahlstrand, and
Joseph Lampel, 1998. New York: The Free Press.
Sarasvathy, S. (2001 ). What makes entrepreneurs
entrepreneurial? Harvard Business Review.
Wernerfelt, B., & Karnani, A. (1987). COMPETITIVE
STRATEGY UNDER UNCERTAINTY. Strategic Management Journal, 187-1 94.