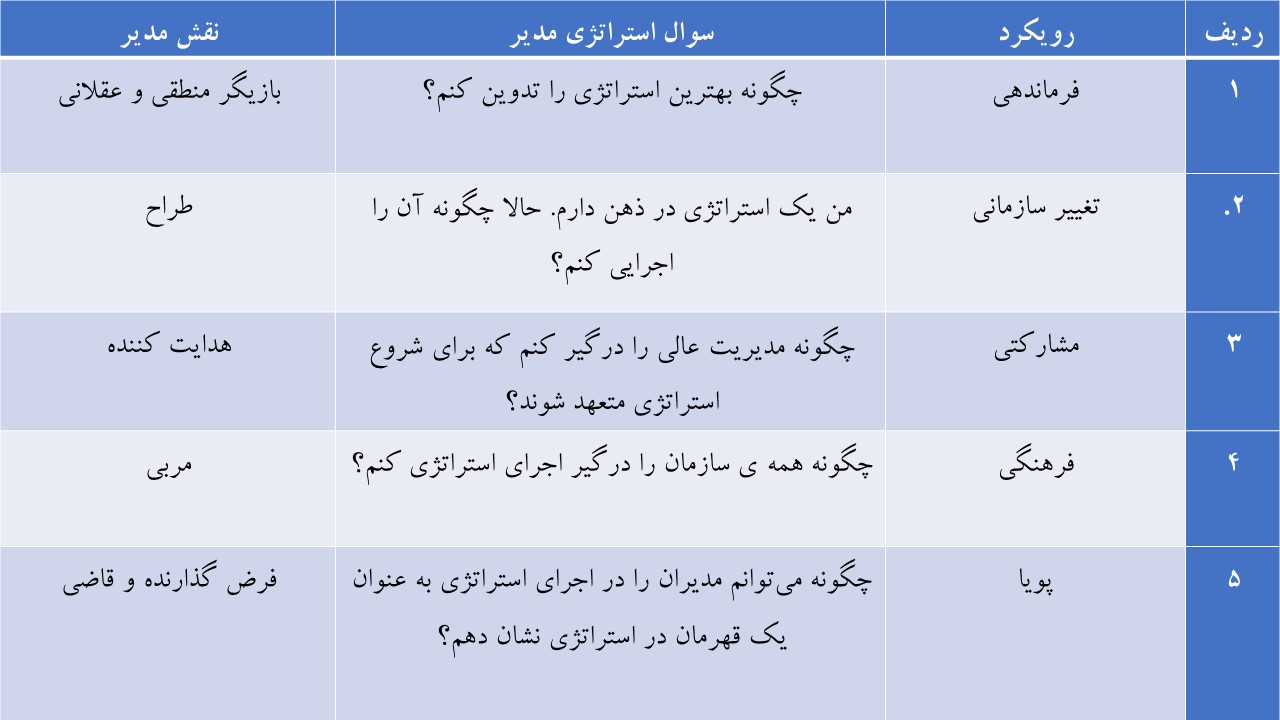
Using integrated solutions as
market-shaping/market-driving strategy in oil industry
Part 5
استفاده از "راه حل یکپارچه" به عنوان استراتژی شکل دهنده بازار و
هدایت کننده بازار در صنعت نفت
بخش پنجم
لینک بخش 4
این پژوهش به عنوان تز پایانی دوره MBA در یکی از دانشگاه های مطرح اروپایی
ارایه شده است
Rational
school of strategy and its formal planning approaches are criticized by process
group (Mintzberg et al, 1998) (Mintzberg
(b), 1987).
They focus on differences between intended, emerging and realized strategy.
Emerging strategy sees strategy as an opportunistic, incremental, and political
process which is done through trial and error and learning. The realized
strategy is the outcome of the both intended and emergent factors. It has been
said that realized strategy is only between 10-30 % of intended strategy (Grant, 2010) (Mintzberg et
al, 1998).
In reality, strategy formation begins with rational approach then moves into a
process mode. In an interesting metaphor Mintzberg (1987) (b) managers are
assumed as craftsmen and strategy as their clay. Like the potter, they sit
between a past of corporate capabilities and a future of market opportunities
and if they are truly craftsmen, they bring to their work an equally intimate
knowledge of the materials at hand; that is the essence of crafting strategy. Classic
approaches to strategy adopt a predictable
future founded on rational assumptions about changes in environment. In a
highly uncertain era, this approach is not an applicable method. Mintzberg
has criticized formal strategic planning schools and recognized four fallacies (Mintzberg et al, 1998):
·
The fallacy of predetermination
·
The fallacy of detachment
·
The fallacy of formalization
·
The grand
fallacy of strategic planning
To explain these fallacies, Mintzberg (1998) states that formal planning
is valuable if the strategy makers can predict the future accurately.
Furthermore, stability and predictability of conditions should be hold not only
during planning but also during implementation. Considering highly uncertain
conditions of today’s business world it is not a realistic assumption. Additionally, since
analysis is not synthesis, formal strategic planning which is based on analysis
cannot be strategy making. Analysis may come first and support synthesis by
providing essential inputs. Via decomposing and formalizing its outcomes,
analysis may follow and expand synthesis.
Considering inability of classic
approaches to strategy in new business world revealing some modern thoughts on
strategy seems necessary. An interesting framework is the portfolio-of-initiatives developed by Bryan (2002)
based on ideas of three horizons of growth and Courtney’s levels of
uncertainty. The framework states that a good strategy should entail “a handful
(portfolio) of good initiatives”. In a further contribution from McKinsey, strategy
is seen as a dialogue, a process which leads to a prepared mind and creativity
in strategy making. The research shows that formal planning can add value if it
has two main goals (Beinhocker & Kaplan, 2002); the first is to
form “prepared minds” to make sure that strategy makers have a concrete
understanding of the business, its strategy and assumptions, environment,
challenges and opportunities, thus making it possible for executives to react swiftly
to challenges and opportunities in real time. The second is to increase the
likelihood that creative insight will occur and consequently the innovativeness
of strategies. Results of another research on 800 executives have shown that
too many companies concentrate on data gathering features of strategic planning
and overlook the vital and critical interactive components (Dye & Sibony, 2007). Hence, team members’
time should be devoted to challenging yet cooperative debates with mangers instead
of struggling to absorb many facts during the review. In other words, the role
of interaction is more important than data gathering (Dye & Sibony, 2007).
لینک به بخش ششم
References:
Beinhocker, E., & Kaplan, S. (2002, June). Tired
of Strategic Planning. Retrieved 2011, from McKinsey Quarterly:
http://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/Tired_of_strategic_planning_1191
Bryan, L. (2002). Just-in-time strategy for a
turbulent world . Mckinsey Quarterly,
https://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/Just-in-time_strategy_for_a_turbulent_world_1195.
Dye, R., & Sibony, O. (2007). The McKinsey
Quarterly. Retrieved 2011, from McKinsey & Company:
https://www.mckinseyquarterly.com/How_to_improve_strategic_planning_2026
Grant, R. (2010). Strategy. Chichester: John
Wiley & Sons.
Mintzberg (b). (1987). Crafting Strategy. Harvard
Business Review, 66-74.
Mintzberg et al. (1998). Strategy Safari: A Guided
Tour Trough the Wilds of Strategic Management", Bruce Ahlstrand, and
Joseph Lampel, 1998. New York: The Free Press.